- Immediate contact :
- +1-323-988-5889
- info@siflaser.com
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1477
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1482
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1503
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1504
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1505
Laser Therapy for Adenocarcinoma Issue
June 6, 2022Laser Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
June 7, 2022Laser Therapy for Vulvar Cancer
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1477
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1482
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1503
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1504
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1505
Vulvar carcinoma is a form of cancer that develops on the female genitalia’s outer surface. The vulva is the skin that covers the urethra and vagina, as well as the clitoris and labia.
Vulvar cancer commonly forms as a lump or sore on the vulva that often causes itching. Though it can occur at any age, vulvar cancer is most commonly diagnosed in older adults.
It is unknown what causes vulvar cancer. In general, experts believe that cancer arises when a cell’s DNA undergoes alterations (mutations). The instructions that inform a cell what to do are included in the DNA. The mutations instruct the cell to expand and divide quickly. When other normal cells die, the cell and its children continue to live. The accumulating cells create a malignant tumor, infecting neighboring tissue and spreading to other regions of the body.
These are the most common signs and symptoms of vulvar cancer:
· Itching that doesn’t go away
· Pain and tenderness
· Bleeding that isn’t from menstruation
· Skin changes, such as color changes or thickening
· A lump, wart-like bumps or an open sore (ulcer)
Vulvar cancer treatment usually involves surgery to remove cancer and a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue. Sometimes vulvar cancer surgery requires removing the entire vulva. The earlier vulvar cancer is diagnosed, the less likely extensive surgery is needed for treatment.
Laser therapy is a cancer treatment that employs the use of a laser beam (a narrow beam of bright light) to destroy cancer cells on the skin’s surface. It is most commonly used to treat vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), as well as vulvar precancerous and non-invasive vulvar carcinoma.
Healing from laser surgery takes at least three weeks but could take up to six weeks or even longer.
Nevertheless, one should never forget that the perfect execution of such a task necessitates a proper and highly professional laser machine.
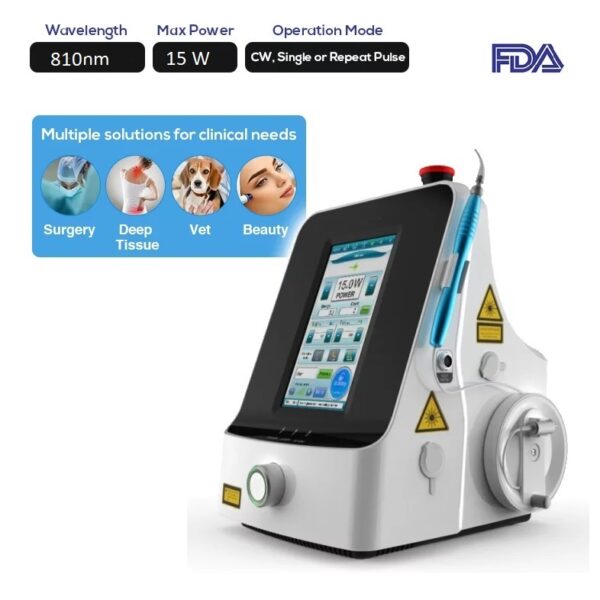
Relatedly, the Portable Surgery 810nm Diode Laser System FDA LASER-1.2A is one of the most recommended equipment among surgeons due to its great efficacy in treating vulvar cancer in particular.
To elaborate, the blue laser light in this technology interacts better with the tissue components haemoglobin or melanin. Even at reduced power, the machine performs better and softer cutting at 980 nm (the high-level laser light required).
Accordingly, its improved cutting performance makes it ideally suited to all surgical applications, particularly Vulvar Cancer non-surgical operations.
What also makes the LASER-1.2A highly appreciated and recommended by surgeons is that it displays an accurate alignment and exact sighting during the treatment. All thanks to its green aiming beam.
To further improve the treatment, the device is supported with a fibre guide laser. So, it is compatible with various endoscopic uses. Also, these special fibres are sterilisable which, in turn, prevents any possible cross-infection while guaranteeing a clean and bloodless operative area.
The device is thought to perfectly address vulvar cancer issues as it enjoys 980 nm wavelength and 15W as maximum power. That is highly attributed to the fact that the LASER-1.2 A uses infrared wavelengths and ultra-blue light to ensure high-level performance. That is also estimated to reduce the thermal damage and its peculiar interaction with haemoglobin.
Due to all these features, the LASER-1.2 A guarantees increased cutting effectiveness, much higher than the one obtained with infrared lasers.
Cancer of the vulva most commonly affects the labia, which are two skin folds (or lips) encircling the vagina. Vulvar carcinoma is a rare disease. However, because it is cancer, it is really dangerous. It can have an impact on a woman’s sexual functioning. Fortunately, laser treatment has lately proven to be helpful in terms of early diagnosis and treatment of this condition, particularly since it has been a successful complement to cancer surgery in general.
On this premise, we endeavored to explain the advantages of laser treatment, specifically the efficacy of LASER-1.2 A as a surgical laser device capable of treating vulvar cancer in women.
Reference: Signs and symptoms of vulvar carcinoma
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFLASER is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each Laser System.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.
Related posts
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type bool in /home/u856774613/domains/siflaser.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/betheme/functions/theme-functions.php on line 1599